[ad_1]
Almost Extinct: Humanity’s Id Stopped a Million Years In the past
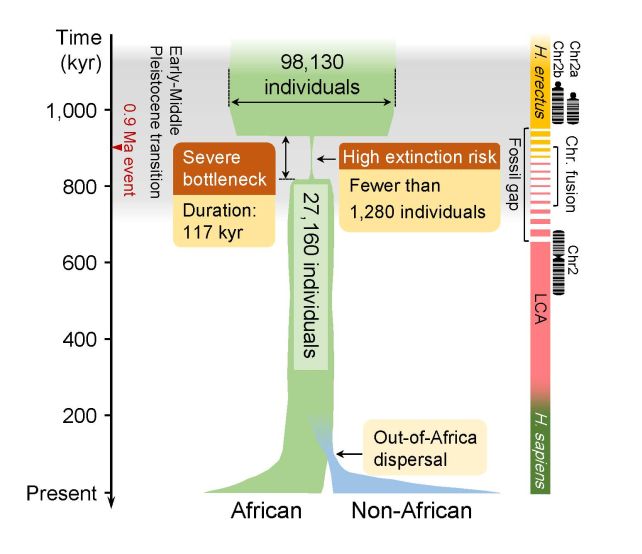
About 1,000,000 years in the past an occasion of catastrophic proportions occurred that threatened the existence of humanity’s ancestors. Based mostly on genomic knowledge from 3,154 trendy people, the inhabitants declined dramatically from about 100,000 to only one,280 reproductive people round 900,000 years in the past. This catastrophic inhabitants decline of 98.7% lasted 117,000 years and probably introduced humanity to the brink of extinction.
Regardless of the severity of those circumstances, the truth that we’re right here in our huge numbers presently serves as a testomony to the resilience of our ancestors. Nevertheless, the outcomes found by a workforce of geneticists led by Haipeng Li of the Chinese language Academy of Linguistics and Yi-Hsuan Pan of East China Common College in China additionally present proof of a wierd hole in human fossil studies. through the Pleistocene interval. ,
Thrills Concerning the Human Fossil Paperwork
Anthropologist Giorgio Manzi of Rome’s Sapienza School in Italy suggests: the variations throughout the African and Eurasian fossil knowledge could also be defined chronologically by this barrier throughout the Early Stone Age. This corresponds to the intense paucity of fossil proof for this proposed time interval.
Habitat constraints, characterised by a major discount in inhabitants numbers, are usually not unusual within the pure world. When a species is devastated by occasions reminiscent of battle, famine, or local weather shock, a discount in genetic choice may be detected within the offspring of the survivors. Extra just lately, proof factors to a human inhabitants bottleneck that occurred within the Northern Hemisphere round 7,000 years in the past. Nevertheless, monitoring again in time presents larger challenges to find crucial alerts.
a model new evaluation technique
For this present research, the analysis workforce developed a novel technique known as the Infinitesimal Brief Time Coalescing Course of (FITCOL). Via the usage of this technique, they had been in a position to take away the buildup of numerical errors that sometimes pertain to previous occasions. The workforce analyzed genomic knowledge from 3,154 people from 10 African and 40 non-African populations utilizing FitCol and famous a extreme inhabitants bottleneck that occurred between 930,000 and 813,000 years in the past. This bottleneck interval resulted within the lack of as much as 65.85% of the current genetic inhabitants.
Trigger and impact of obstruction
The exact clarification of this bottleneck stays unsure. Nevertheless, there was one main occasion throughout that interval that clearly performed a task: the Center Pleistocene transition, marked by dramatic modifications to Earth’s glacial cycles. It’s believable that the ensuing local weather instability created unfavorable situations for human populations struggling to outlive, leading to famine, battle, and extra reductions in inhabitants numbers.
Yi-Hsuan Pan expresses: The novel discovery opens up a brand new vista in human evolution as a result of it raises many questions, such because the locations these individuals lived, how they overcame catastrophic local weather modifications, and whether or not they had been ‘pure’. sure. Constraints in addition to choice have accelerated the event of human thought.
Formation of chromosome 2 and human growth
The bottleneck occasion additionally seems to have affected an fascinating position of the human genome: the fusion of two chromosomes to type chromosome 2. Whereas trendy people have 23 pairs of chromosomes, all different hominids, together with nice apes, have 24 pairs. The formation of chromosome 2 seems to be a speciation occasion that led people to observe a selected evolutionary path.
Haipeng Li says: These findings are just the start. Future pursuits with this knowledge intention to color a extra full image of human evolution throughout this transitional interval from the early to center Pleistocene, which can proceed to unravel the thriller of early human ancestry and evolution.
conclusion
This groundbreaking research, led by Haipeng Li and Yi-Hsuan Pan, sheds mild on an necessary facet of human historical past a whole bunch of years in the past. The invention of the overpopulation barrier that drove humanity to the brink of extinction provides a brand new chapter to our understanding of our historical past. This analysis not solely explains a serious hole in human fossil studies through the Pleistocene, but additionally raises fascinating questions concerning the challenges our ancestors confronted and the long-term influence on human evolution.
Often Requested Questions (FAQs)
1. What is supposed by inhabitants constraint?
The inhabitants bottleneck, the place humanity’s ancestors had been diminished to a mere fraction of their unique numbers, is a crucial occasion in our evolutionary historical past. It highlights the resilience and resilience of the primitive individuals who managed to outlive and flourish in opposition to all odds.
2. How was the inhabitants bottleneck studied?
The analysis workforce developed a novel technique known as FitCol, which allowed them to research genomic knowledge from 3,154 trendy individuals. This technique overcame challenges related to studying occasions from the previous, permitting them to work out the small print of the inhabitants constraint.
3. Why did the residents come to a standstill?
Though the precise trigger stays unsure, a serious occasion that will have performed a task is the Center Pleistocene transition, marked by vital modifications in Earth’s glacial cycles. The ensuing local weather instability created unfavorable situations for early human populations, leading to famine, battle, and extra discount in numbers.
4. How did habitat constraints have an effect on human evolution?
The inhabitants bottleneck influenced the human genome by contributing to the fusion of the 2 chromosomes, ensuing within the formation of chromosome 2. This species likelihood set individuals on a selected evolutionary path that units us aside from different hominids. ,
5. What are the long run goals of this evaluation?
The researchers intend to delve deeper into human evolution through the transition interval from the Early Pleistocene to the Center Pleistocene. They wish to discover out extra concerning the lives of our ancestors, how they tailored to catastrophic local weather modifications, and what constraints drove the evolution of the human mind.
For added knowledge, see this hyperlink
[ad_2]
To entry extra data, kindly check with the next link
